Published 2021-01-26
Using Amazon API Gateway (Rest API) with Swift Lambda - Part 1
Amazon have two different API Gateway services that can be used for connecting other AWS services, like Lambda, to HTTP endpoints. They are API Gateway (Rest API), and HTTP API. The API HTTP (apigatewayv2) is the newest service, and the easiest to configure, but the Rest API (apigateway) is the service with the most functionality but also the most complicated one. In this three-part blog posts we will focus on the Rest API.
We will go through three integrations with Lambda, this first post will show you how to use the API Gateway to integrate with a GET method with query parameters. This means that you will be able to use a normal web browser to connect to the Lambda service, and supply parameters through the browsers query parameters. The next two posts will show how to integrate with a POST method with a JSON payload to get the same result, and the third blog post will show how to integrate with a GET method with path parameters.
The nice thing about this is that we don't have to modify the Swift Lambda code to integrate with these three different methods, all is done with using API Gateway and the supporting services.
I have used the AWS Tutorial from Amazon as an inspiration for these three blog posts, but I will be using the aws cli to set up everything, instead of using the AWS consoles from a browser.
The code for this blog post can be cloned from lambda-calc1 GitHub repository.
Swift Lambda code
The Lambda function is a simple function that acts as a simple calculator, and the parameters supplied to the function are the two numbers the function is to operate on, and one of the 4 operators (add, sub, mul, div).
We will make the new Lambda function by first making a new folder and then use Swift to init a new SPM project:
mkdir calc && cd calc
swift package init --type executable
We can open the project in Xcode by double-clicking the Package.swift file in Finder, or by doing open Package.swift in the Terminal.
Add AWSLambdaRuntime to the Package.swift file:
// swift-tools-version:5.3
// The swift-tools-version declares the minimum version of Swift required to build this package.
import PackageDescription
let package = Package(
name: "calc",
dependencies: [
.package(url: "https://github.com/swift-server/swift-aws-lambda-runtime.git", .upToNextMajor(from: "0.3.0"))
],
targets: [
// Targets are the basic building blocks of a package. A target can define a module or a test suite.
// Targets can depend on other targets in this package, and on products in packages this package depends on.
.target(
name: "calc",
dependencies: [
.product(name: "AWSLambdaRuntime", package: "swift-aws-lambda-runtime")
]),
.testTarget(
name: "calcTests",
dependencies: ["calc"]),
]
)
Add the code for the simple calculator to main.swift:
import AWSLambdaRuntime
struct Input: Codable {
enum Operation: String, Codable {
case add
case sub
case mul
case div
}
let a: Double
let b: Double
let op: Operation
}
struct Output: Codable {
let result: Double
}
Lambda.run { (context, input: Input, callback: @escaping (Result<Output, Error>) -> Void) in
let result: Double
switch input.op {
case .add:
result = input.a + input.b
case .sub:
result = input.a - input.b
case .mul:
result = input.a * input.b
case .div:
result = input.a / input.b
}
callback(.success(Output(result: result)))
}
Test Lambda function with Xcode
Select edit scheme in Xcode: 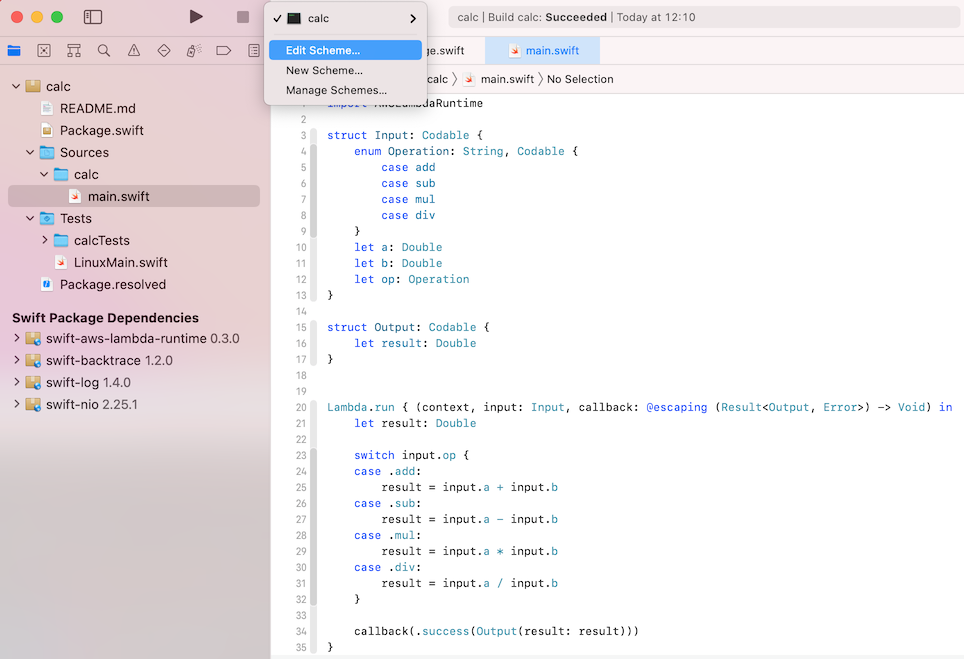
Add the environment variable LOCAL_LAMBDA_SERVER_ENABLED, and set the value to true: 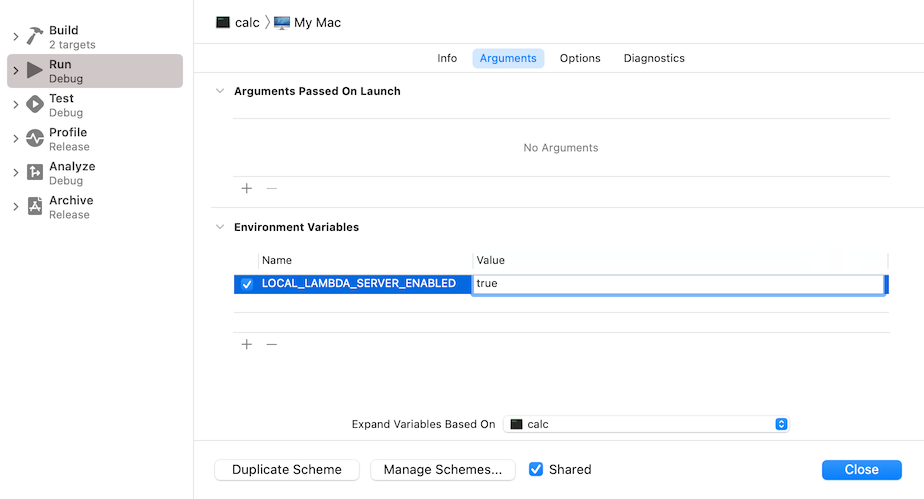
Click the Run button in Xcode, and try with a similar curl command as this:
curl -i --request POST \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{"a": 8, "b": 6, "op": "mul"}' \http://localhost:7000/invoke
This should return a JSON with:
{"result":48}
Scripts
Visual Studio Code is an excellent editor, and I will use it for the rest of this tutorial. Make a new folder scripts, and add a file with name setup_aws.sh to it: 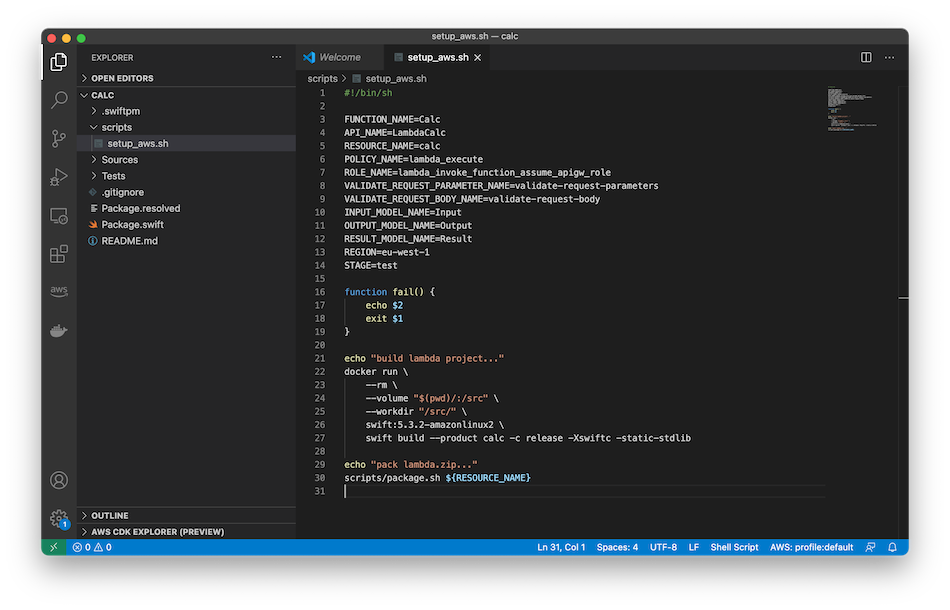
The following are the constants used in the script:FUNCTION_NAME=Calc
The named used for the Lambda function.
API_NAME=LambdaCalc
The name we give to the Rest API in API Gateway.
RESOURCE_NAME=calc
The resource name given to the API Gateway resource. This name is also used in the endpoint url to the Lambda function.
POLICY_NAME=lambda_execute
The name of the iam policy we use to attach to the iam role.
ROLE_NAME=lambda_invoke_function_assume_apigw_role
The name of the execution role of the Lambda function.
VALIDATE_REQUEST_PARAMETER_NAME
The name of the request validator we use in API Gateway to validate the query parameters.
REGION
The name of the aws region.
STAGE
The name of the stage.
We must compile and pack the Lambda function with Amazon Linux 2, so it can run on the AWS cloud platform. Luckily, we have a swift image prepared for Amazon Linux 2, so we can use docker to compile our Lambda function. The following command is added to the script to produce the compiled lambda function:
docker run \
--rm \
--volume "$(pwd)/:/src" \
--workdir "/src/" \swift:5.3.2-amazonlinux2 \swift build --product calc -c release -Xswiftc -static-stdlib
Check out the excellent blog post (Step 5) by Fabian Fett for an explanation of the parameters.
The scripts/packagage.sh ${RESOURCE_NAME} at the end of the script packs the script in in a zip file.
Add the package.sh shell script to the scripts folder:
#!/bin/bash
set -eu
executable=$1
target=.build/lambda/$executable
rm -rf "$target"
mkdir -p "$target"
cp ".build/release/$executable" "$target/"
cd "$target"
ln -s "$executable" "bootstrap"
zip --symlinks lambda.zip *
Make the scripts executable with chmod +x scripts/package.sh scripts/setup_aws.sh
When we run the setup_aws.sh, the zipped file can be found under .build/lambda/calc/lambda.zip
AWS API Gateway setup
The setup of the AWS infrastructure to make API Gateway work is a bit complicated, so we will add aws cli commands to the setup_aws.sh file for this. The aws cli is easiest installed with brew install awscli.
Another shell script delete_aws.sh is used to tear down the infrastructure in AWS. This makes it easier to handle the complicated setup.
The setup script stores the results of the scripts in the results/aws folder, so we have to make this folder first with mkdir -p results/aws
I will explain the steps made in the setup script, but the complete project with swift code and the scripts can be cloned from my GitHub repository.
IAM role and policy
We need to create an execution role for the Lambda function, and an iam policy to attach to the role. Make the json file with the policy with name Invoke-Function-Role-Trust-Policy.json:
{
"Version":"2012-10-17",
"Statement":[
{
"Effect":"Allow",
"Action":"lambda:InvokeFunction",
"Resource":"*"
}
]
}
Add the command for creating the policy to setup_aws.sh:
echo "1 iam create-policy..."
aws iam create-policy \
--policy-name $POLICY_NAME \
--policy-document file://Invoke-Function-Role-Trust-Policy.json \
> results/aws/create-policy.json
[ $? == 0 ] || fail 1 "Failed: AWS / iam / create-policy"
POLICY_ARN=$(aws iam list-policies --query "Policies[?PolicyName==\`${POLICY_NAME}\`].Arn" --output text --region ${REGION})
We are storing the policy arn in POLICY_ARN, we need this when we will attach the policy to the role.
Before we can create the role, we need another policy, Assume-STS-Role-Policy.json file:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": [
"lambda.amazonaws.com",
"apigateway.amazonaws.com"
]
},
"Action": "sts:AssumeRole"
}
]
}
Now we can create the role:
echo "2 iam create-role..."
aws iam create-role \
--role-name $ROLE_NAME \
--assume-role-policy-document file://Assume-STS-Role-Policy.json \
> results/aws/create-role.json
[ $? == 0 ] || fail 2 "Failed: AWS / iam / create-role"
And we can attach the policy we created in step 1:
echo "3 iam attach-role-policy..."
aws iam attach-role-policy \
--role-name $ROLE_NAME \
--policy-arn $POLICY_ARN \
> results/aws/attach-role-policy.json
[ $? == 0 ] || fail 3 "Failed: AWS / iam / attach-role-policy"
ROLE_ARN=$(aws iam list-roles --query "Roles[?RoleName==\`${ROLE_NAME}\`].Arn" --output text --region ${REGION})
ROLE_ARN keeps the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) value for the role we created. ARN is an identifier that unambigiously identifies a resource across all of AWS.
Create Lambda function
Before we create the function, we makes the shell script sleep for 10 seconds with the sleep 10 before the create-function. This is because the create-role and attach-role-policy takes some time to be ready before it can be used in the create-function command. The command failed until I did this.
sleep 10
echo "4 lambda create-function..."
aws lambda create-function \
--region ${REGION} \
--function-name ${FUNCTION_NAME} \
--runtime provided.al2 \
--handler lambda.run \
--memory-size 128 \
--zip-file fileb://.build/lambda/calc/lambda.zip \
--role ${ROLE_ARN} \
> results/aws/lambda-create-function.json
[ $? == 0 ] || fail 4 "Failed: AWS / lambda / create-function"
LAMBDA_ARN=$(aws lambda list-functions --query "Functions[?FunctionName==\`${FUNCTION_NAME}\`].FunctionArn" --output text --region ${REGION})
The LAMBDA_ARN keeps the arn of the Lambda function, to be used later. Notice that we use the runtime provided.al2, which is the amazon linux2 runtime. And the zip-file is the path to the lambda.zip we produced with the package.sh shell script.
API Gateway commands
The rest of the commands in this shell script are the API Gateway commands that are needed to create the REST API for the Lambda function.
echo "5 apigateway create-rest-api..."
aws apigateway create-rest-api \
--region ${REGION} \
--name ${API_NAME} \
--endpoint-configuration types=REGIONAL \
> results/aws/create-rest-api.json
[ $? == 0 ] || fail 5 "Failed: AWS / apigateway / create-rest-api"
API_ID=$(aws apigateway get-rest-apis --query "items[?name==\`${API_NAME}\`].id" --output text --region ${REGION})
PARENT_RESOURCE_ID=$(aws apigateway get-resources --rest-api-id ${API_ID} --query 'items[?path==`/`].id' --output text --region ${REGION})
This is the command for the creation of the API Gateway itself. API_ID is the id of the REST API we have created, and is used in almost all of the rest of the commands. We also need to save the PARENT_RESOURCE, which is the root resource we need for creation of new resources for the REST API.
The first resource we create is the calc resource, which will be part of the path to the next resource:
echo "6 apigateway create-resource..."
aws apigateway create-resource \
--region ${REGION} \
--rest-api-id ${API_ID} \
--parent-id ${PARENT_RESOURCE_ID} \
--path-part ${RESOURCE_NAME} \
> results/aws/create-resource.json
[ $? == 0 ] || fail 6 "Failed: AWS / apigateway / create-resource"
RESOURCE_ID=$(aws apigateway get-resources --rest-api-id ${API_ID} --query "items[?path==\`/$RESOURCE_NAME\`].id" --output text --region ${REGION})
We save the id of this resource in RESOURCE_ID. It is used in the put-method in step 8. We can make the API Gateway validate the request query parameters we supply in the URI of the request, so that we don't call the Lambda function with wrong parameters. We do that with the request validators we create in step 7.
echo "7 apigateway create-request-validator..."
aws apigateway create-request-validator \
--region ${REGION} \
--rest-api-id ${API_ID} \
--name ${VALIDATE_REQUEST_PARAMETER_NAME} \
--validate-request-parameters \
> results/aws/create-request-parameters-validator.json
[ $? == 0 ] || fail 7 "Failed: AWS / apigateway / create-request-validator"
REQUEST_VALIDATOR_PARAMETERS_ID=$(aws apigateway get-request-validators --rest-api-id ${API_ID} --query "items[?name==\`$VALIDATE_REQUEST_PARAMETER_NAME\`].id" --output text --region ${REGION})
Now we have reached the point where we will do the integrations. This blog post will make the first integration, with the /calc/GET method. The next blog posts will show how to do integrations with POST and GET paths.
Integration 1
#Integration 1
# Resources /calc/GET
echo "8 apigateway put-method..."
aws apigateway put-method \
--region ${REGION} \
--rest-api-id ${API_ID} \
--resource-id ${RESOURCE_ID} \
--http-method GET \
--authorization-type NONE \
--request-validator-id ${REQUEST_VALIDATOR_PARAMETERS_ID} \
--request-parameters "method.request.querystring.operand1=true,method.request.querystring.operand2=true,method.request.querystring.operator=true" \
> results/aws/put-get-method.json
[ $? == 0 ] || fail 8 "Failed: AWS / apigateway / put-method"
We see that we create the GET http-method, and we also validate the three querystring parameters operand1, operand2 and operator. API Gateway will make an error if one of these parameters are missing, or have wrong names.
echo "9 apigateway put-method-response..."
aws apigateway put-method-response \
--region ${REGION} \
--rest-api-id ${API_ID} \
--resource-id ${RESOURCE_ID} \
--http-method GET \
--status-code 200 \
--response-models application/json=Empty \
> results/aws/put-method-response.json
[ $? == 0 ] || fail 9 "Failed: AWS / apigateway / put-method-response"
We return statuscode 200 if we don't have any errors in the Lambda code. In this example we just return the response from the Lambda code directly, and don't use any response models to modify the result.
Before the next step, we need to make a new JSON file for the request templates in the put-integration command. Make a new file with name request-templates.json with content:
{
"application/json":"{\n \"a\": $input.params('operand1'),\n \"b\": $input.params('operand2'), \n \"op\": \"$input.params('operator')\" \n}"
}
We see here that we map the input parameter operand1 to the a parameter of the Lambda function, operand2 to the b parameter and operator to the op parameter, exactly as we have it in the Input Swift struct in our Calc Lambda function.
Now we can make the integration. Note that we use type AWS as the integration type. If we had chosen AWS_PROXY instead, we would not have the option to set the mappings of the request and response, like we want to show in this blog post, nor use the GET method to supply the parameters as query parameters in the URI.
Check out the Choose an API Gateway API integration type for the different types we can use.
echo "10 apigateway put-integration..."
aws apigateway put-integration \
--region ${REGION} \
--rest-api-id ${API_ID} \
--resource-id ${RESOURCE_ID} \
--http-method GET \
--type AWS \
--integration-http-method POST \
--uri arn:aws:apigateway:${REGION}:lambda:path/2015-03-31/functions/${LAMBDA_ARN}/invocations \
--credentials ${ROLE_ARN} \
--passthrough-behavior WHEN_NO_TEMPLATES \
--request-templates file://request-templates.json \
> results/aws/put-get-integration.json
[ $? == 0 ] || fail 10 "Failed: AWS / apigateway / put-integration"
We are at last come to the last command for this integration. That is the integration response. Make sure that the response-templates is set to application/json with a value of null, which is set with the empty quotes in the command.
echo "11 apigateway put-integration-response..."
aws apigateway put-integration-response \
--region ${REGION} \
--rest-api-id ${API_ID} \
--resource-id ${RESOURCE_ID} \
--http-method GET \
--status-code 200 \
--response-templates application/json="" \
> results/aws/put-get-integration-response.json
[ $? == 0 ] || fail 11 "Failed: AWS / apigateway / put-integration-response"
Deploy the API Gateway
We can now deploy the API Gateway :
echo "12 apigateway create-deployment..."
aws apigateway create-deployment \
--region ${REGION} \
--rest-api-id ${API_ID} \
--stage-name ${STAGE} \
> results/aws/create-deployment.json
[ $? == 0 ] || fail 12 "Failed: AWS / apigateway / create-deployment"
Add the following to the end of the script, so that we at the end of execution of the script can output the endpoint and test it with a simple curl command:
ENDPOINT=https://${API_ID}.execute-api.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/${STAGE}/calc
echo "API available at: ${ENDPOINT}"
echo
echo "Integration 1"
echo "Testing GET with query parameters:"
echo "27 / 9"
cat << EOF
curl -i --request GET \
https://${API_ID}.execute-api.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/${STAGE}/calc\?operand1\=27\&operand2\=9\&operator\=div
EOF
echo
curl -i --request GET \
https://${API_ID}.execute-api.eu-west-1.amazonaws.com/${STAGE}/calc\?operand1\=27\&operand2\=9\&operator\=div
Testing
Run the command scripts/setup_aws.sh in the terminal. This will compile the Swift Lambda function, pack it in a zip file, and run all the aws commands. Hopefully all the steps will be executed successfully, and we will have and endpoint printed out which we can use to test the function.
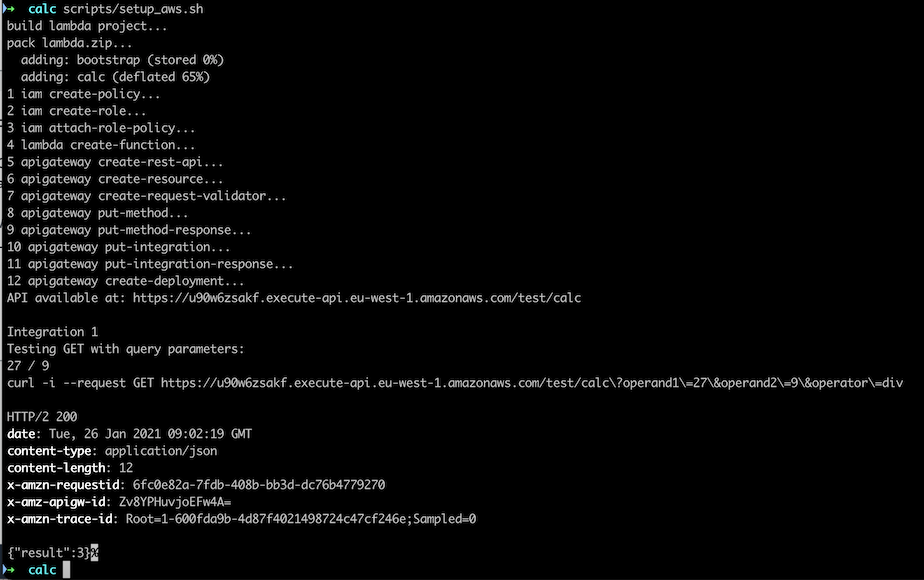
Test with Safari, and give a wrong query parameter (operator2) instead of operand2. We see that we get an error from API Gateway, before we hit the Lambda function: 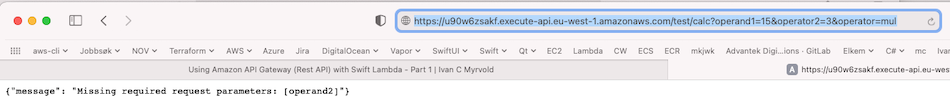
Now replace operator2 with operand2, and we should get a correct result: 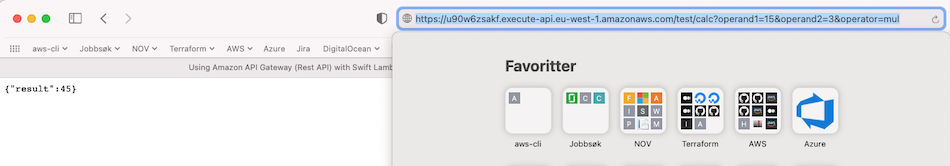
Cleanup
To remove the Lambda function and the API Gateway, add this file to the scripts folder, with the name delete_aws.sh:
#!/bin/sh
FUNCTION_NAME=Calc
API_NAME=LambdaCalc
POLICY_NAME=lambda_execute
ROLE_NAME=lambda_invoke_function_assume_apigw_role
REGION=eu-west-1
POLICY_ARN=$(aws iam list-policies --query "Policies[?PolicyName==\`${POLICY_NAME}\`].Arn" --output text --region ${REGION})
aws iam detach-role-policy \
--role-name $ROLE_NAME \
--policy-arn $POLICY_ARN
aws iam delete-policy \
--policy-arn $POLICY_ARN
aws iam delete-role \
--role-name $ROLE_NAME
API_ID=$(aws apigateway get-rest-apis --query "items[?name==\`${API_NAME}\`].id" --output text --region ${REGION})
aws apigateway delete-rest-api \
--rest-api-id ${API_ID}
aws lambda delete-function \
--function-name $FUNCTION_NAME
Make the script executable with chmod +x scripts/delete_aws.sh.
Run the command with scripts/delete_aws.sh to remove everything you set up with the setup_aws.sh script.