Published 2021-01-02
Make a continuous delivery of Swift Lambda in AWS
I showed in my previous post how to make a Lambda function in AWS. Wouldn't it be great to have any changes of the source code in the Lambda function trigger a continuous delivery/deployment of the Lambda function in AWS? This is what this post is about. We will use CDK to set up a pipeline in AWS so that any changes in the Lambda code you push to GitHub will automatically install a revised Lambda function in AWS without you ever think about it.
Thanks to Fabian Fett for his blog post where he connects API Gateway to a Swift Lambda function, and Alfian Losari for his Building Swift Serverless REST API with AWS Lambda & DynamoDB blog post. It made it much easier to write this blog post.
If you want to follow along coding this on your own Mac, you must have Node Package Manager installed. That is easiest installed with Homebrew:
brew install node
Set up the Lambda project
You can clone the source of this project from my GitHub repository.
Make a new directory, and make a Swift project:
mkdir SquareNumber && cd SquareNumber
swift package init --type executable
Initialize git with:
git init
Because of a bug in cdk, we need to add cdk* to .dockerignore for the cdk synth command to work properly:
echo 'cdk*' > .dockerignore
We can start up Xcode with:
open Package.swift
Modify Package.swift to add swift-aws-lambda-runtime package:
// swift-tools-version:5.3
// The swift-tools-version declares the minimum version of Swift required to build this package.
import PackageDescription
let package = Package(
name: "SquareNumber",
dependencies: [
.package(url: "https://github.com/swift-server/swift-aws-lambda-runtime.git", .upToNextMajor(from: "0.3.0"))
],
targets: [
// Targets are the basic building blocks of a package. A target can define a module or a test suite.
// Targets can depend on other targets in this package, and on products in packages this package depends on.
.target(
name: "SquareNumber",
dependencies: [
.product(name: "AWSLambdaRuntime", package: "swift-aws-lambda-runtime"),
.product(name: "AWSLambdaEvents", package: "swift-aws-lambda-runtime")
]),
.testTarget(
name: "SquareNumberTests",
dependencies: ["SquareNumber"]),
]
)
Replace the content of main.swift with this:
import AWSLambdaRuntime
import AWSLambdaEvents
import NIO
import Foundation
struct Input: Codable {
let number: Double
}
struct Output: Codable {
let result: Double
}
struct SquareNumberHandler: EventLoopLambdaHandler {
typealias In = APIGateway.V2.Request
typealias Out = APIGateway.V2.Response
func handle(context: Lambda.Context, event: In) -> EventLoopFuture<APIGateway.V2.Response> {
guard let input: Input = try? event.bodyObject() else {
return context.eventLoop.makeSucceededFuture(APIGateway.V2.Response(with: APIError.requestError, statusCode: .badRequest))
}
let output = Output(result: input.number * input.number)
let apigatewayOutput = APIGateway.V2.Response(with: output, statusCode: .ok)
return context.eventLoop.makeSucceededFuture(apigatewayOutput)
}
}
Lambda.run(SquareNumberHandler())
Make a new file in Xcode with name APIError.swift, with content:
import Foundation
enum APIError: Error {
case decodingError
case requestError
}
Make a new folder extensions with the two files APIGateway.Request+bodyObject.swift and APIGateway.Response+init.swift:
import AWSLambdaEvents
import Foundation
extension APIGateway.V2.Request {
func bodyObject<D: Decodable>() throws -> D {
guard let jsonData = body?.data(using: .utf8) else { throw APIError.requestError }
let decoder = JSONDecoder()
let object = try decoder.decode(D.self, from: jsonData)
return object
}
}
APIGateway.Request+bodyObject.swift
import AWSLambdaEvents
import Foundation
extension APIGateway.V2.Response {
public static let defaultHeaders = [
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Access-Control-Allow-Origin": "*",
"Access-Control-Allow-Methods": "OPTIONS,GET,POST,PUT,DELETE",
"Access-Control-Allow-Credentials": "true"
]
public init(with error: Error, statusCode: AWSLambdaEvents.HTTPResponseStatus) {
self.init(
statusCode: statusCode,
headers: APIGateway.V2.Response.defaultHeaders,
multiValueHeaders: nil,
body: "{\"error\":\"\(String(describing: error))\"}",
isBase64Encoded: false
)
}
public init<Out: Encodable>(with object: Out, statusCode: AWSLambdaEvents.HTTPResponseStatus) {
var body: String = "{}"
let encoder = JSONEncoder()
if let data = try? encoder.encode(object) {
body = String(data: data, encoding: .utf8) ?? body
}
self.init(
statusCode: statusCode,
headers: APIGateway.V2.Response.defaultHeaders,
multiValueHeaders: nil,
body: body,
isBase64Encoded: false
)
}
}
struct EmptyResponse: Encodable {}
APIGateway.Response+init.swift
Test locally with Xcode
Open Xcode, and select Edit Scheme...: 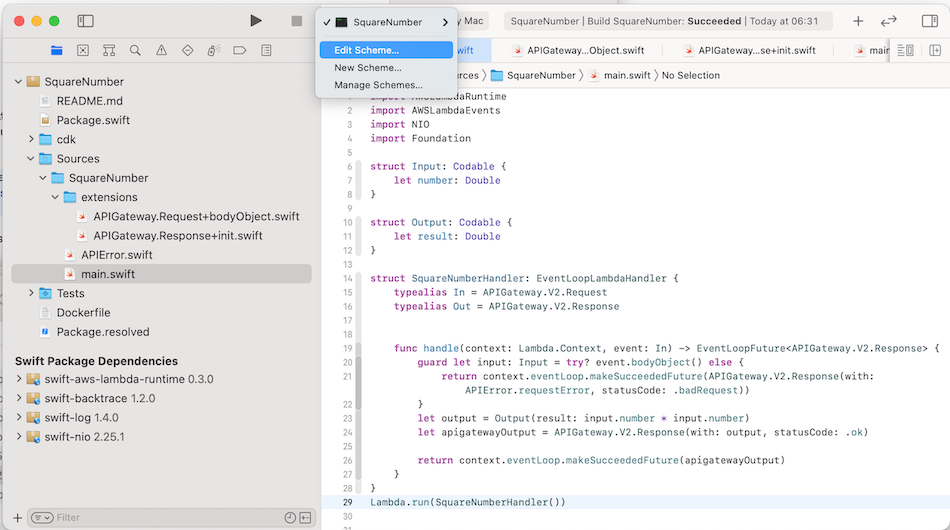
Set the environment variable LOCAL_LAMBDA_SERVER_ENABLED to true: 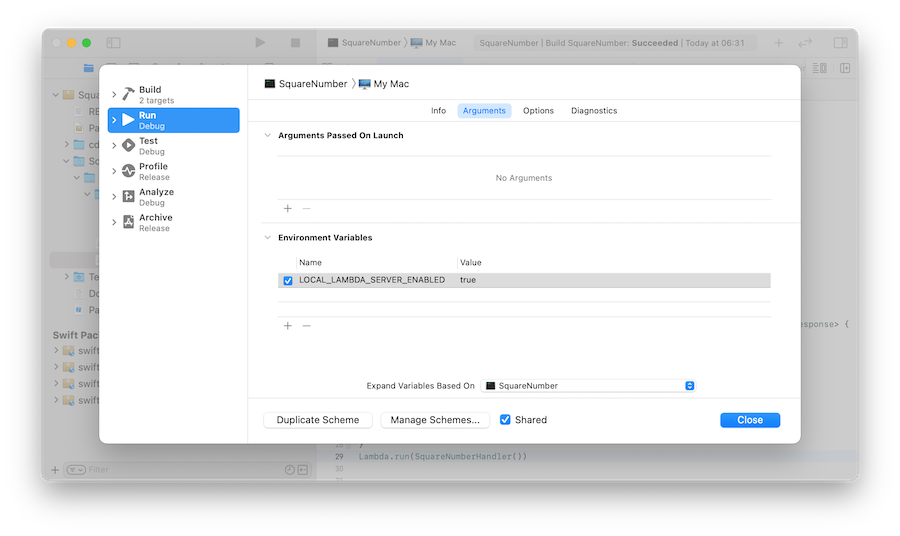
Now you can curl to localhost at port 7000. The format of the POST request is the same format that the lambda function receives from the API Gateway in AWS: 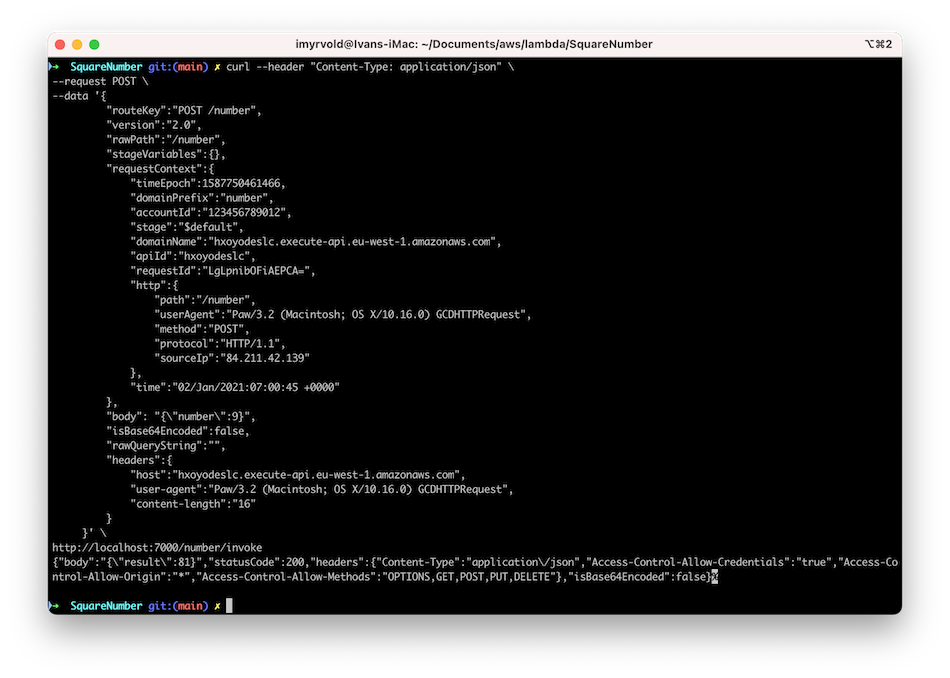 We are sending the
We are sending the number 9 in the body, and we receive 81 in the result. Excellent!
Set up the infrastructure code with CDK
With the Terminal cli, at the root of the project, make a new cdk folder and navigate to it with:
mkdir cdk && cd cdk
Initialize it with:
cdk init --language typescript
I am choosing typescript as a language here, but you can choose between JavaScript, Python, C#, Java and soon also Go.
This will initialize the CDK folder with a blank CDK project and install @aws-cdk/core npm packet.
You need to install extra packages:
npm install @aws-cdk/aws-lambda @aws-cdk/aws-codepipeline @aws-cdk/aws-codepipeline-actions @aws-cdk/aws-ecr @aws-cdk/pipelines @aws-cdk/aws-apigatewayv2 @aws-cdk/aws-apigatewayv2-integrations @aws-cdk/aws-cloudfront
Open Visual Studio Code with:
open -a Visual\ Studio\ Code .
Check package.json to see all the packages installed.
Rename lib/cdk-stack.ts to lib/square-number-cicd-infra.ts.
Replace the content of square-number-cicd-infra.ts with this:
import * as cdk from '@aws-cdk/core';
import * as codepipeline from '@aws-cdk/aws-codepipeline';
import * as codepipeline_actions from '@aws-cdk/aws-codepipeline-actions';
import * as ecr from '@aws-cdk/aws-ecr';
import * as iam from '@aws-cdk/aws-iam';
import * as pipelines from '@aws-cdk/pipelines';
import { LambdaDeploymentStage } from './lambda-deployment';
export class SquareNumberCicdInfraStack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: cdk.Construct, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props)
const sourceArtifact = new codepipeline.Artifact();
const cdkOutputArtifact = new codepipeline.Artifact();
const buildArtifact = new codepipeline.Artifact();
const pipeline = new pipelines.CdkPipeline(this, 'CdkPipeline', {
crossAccountKeys: false,
pipelineName: 'square-number-pipeline',
cloudAssemblyArtifact: cdkOutputArtifact,
sourceAction: new codepipeline_actions.GitHubSourceAction({
actionName: 'DownloadSources',
owner: 'imyrvold',
repo: 'SquareNumberCICD',
branch: 'main',
oauthToken: cdk.SecretValue.secretsManager('github-token'),
output: sourceArtifact
}),
synthAction: pipelines.SimpleSynthAction.standardNpmSynth({
sourceArtifact: sourceArtifact,
cloudAssemblyArtifact: cdkOutputArtifact,
subdirectory: 'cdk'
})
});
const repository = new ecr.Repository(this, 'Repository', { repositoryName: 'cdk-cicd/square-number'});
const buildRole = new iam.Role(this, 'DockerBuildRole', {
assumedBy: new iam.ServicePrincipal('codebuild.amazonaws.com')
});
repository.grantPullPush(buildRole);
const lambdaStage = new LambdaDeploymentStage(this, 'LambdaDeploymentStage');
pipeline.addApplicationStage(lambdaStage);
}
}
This file defines the infrastructure in AWS that is needed to set up a CI/CD pipeline. The pipeline consists of two stages, the DownloadSources stage that pulls the source code of the whole project from GitHub, and the LambdaDeploymentStage that deploys the lambda function in AWS.
The deployment stage instantiates the SquareNumberLambdaStack which is defined in the square-number-lambda-stack.ts which you will define under lib. Add the file lib/square-number-lambda-stack.ts with the following content:
import * as cdk from '@aws-cdk/core';
import * as lambda from '@aws-cdk/aws-lambda';
import * as apigatewayv2 from '@aws-cdk/aws-apigatewayv2';
import { LambdaProxyIntegration } from '@aws-cdk/aws-apigatewayv2-integrations';
import { CloudFrontWebDistribution } from '@aws-cdk/aws-cloudfront';
export class SquareNumberLambdaStack extends cdk.Stack {
constructor(scope: cdk.Construct, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
const dockerfile = '../';
const squareNumberLambdaFunction = new lambda.DockerImageFunction(this, 'SquareNumberLambdaFunction', {
functionName: 'SquareNumber',
code: lambda.DockerImageCode.fromImageAsset(dockerfile)
});
const httpApiIntegration = new LambdaProxyIntegration({
handler: squareNumberLambdaFunction,
});
const api = new apigatewayv2.HttpApi(this, 'SquareNumberApi', {
createDefaultStage: true,
corsPreflight: {
allowMethods: [ apigatewayv2.HttpMethod.POST ],
allowOrigins: ['*']
}
});
api.addRoutes({
path: '/number',
integration: httpApiIntegration,
methods: [apigatewayv2.HttpMethod.POST]
});
const feCf = new CloudFrontWebDistribution(this, "MyCf", {
defaultRootObject: "/",
originConfigs: [{
customOriginSource: {
domainName: `${api.httpApiId}.execute-api.${this.region}.${this.urlSuffix}`,
},
behaviors: [{
isDefaultBehavior: true,
}],
}],
enableIpV6: true,
});
new cdk.CfnOutput(this, "myOut", {
value: feCf.distributionDomainName,
});
}
}
And the last file to add is the lambda-deployment.ts file. Add the lib/lambda-deployment.ts file with the following content:
import * as cdk from '@aws-cdk/core';
import { SquareNumberLambdaStack } from './square-number-lambda-stack';
export class LambdaDeploymentStage extends cdk.Stage {
constructor(scope: cdk.Construct, id: string, props?: cdk.StackProps) {
super(scope, id, props);
const lambdaStack = new SquareNumberLambdaStack(this, 'SquareNumberLambdaStack');
}
}
In the file bin/cdk.ts update the file to this:
#!/usr/bin/env node
import * as cdk from '@aws-cdk/core';
import { SquareNumberCicdInfraStack } from '../lib/square-number-cicd-infra';
const app = new cdk.App();
new SquareNumberCicdInfraStack(app, 'SquareNumberCicdInfraStack');
app.synth();
We need to bootstrap the project, to add some new functionality for the CI/CD pipeline in CDK to work. For that to work, we need to add this line to the cdk.json file:
"@aws-cdk/core:newStyleStackSynthesis": true
Make sure that the file looks like this:
{
"app": "npx ts-node --prefer-ts-exts bin/cdk.ts",
"context": {
"@aws-cdk/core:enableStackNameDuplicates": "true",
"aws-cdk:enableDiffNoFail": "true",
"@aws-cdk/core:stackRelativeExports": "true",
"@aws-cdk/aws-ecr-assets:dockerIgnoreSupport": true,
"@aws-cdk/aws-secretsmanager:parseOwnedSecretName": true,
"@aws-cdk/aws-kms:defaultKeyPolicies": true,
"@aws-cdk/core:newStyleStackSynthesis": true
}
}
At last, we need the Dockerfile so that we can build a new docker image for the lambda function. Make a new file with name Dockerfile with this content:
FROM public.ecr.aws/o8l5c1i1/swift:5.3.2-amazonlinux2 as build
WORKDIR /src
COPY . .
RUN swift build --product SquareNumber -c release -Xswiftc -static-stdlib
FROM public.ecr.aws/lambda/provided:al2
COPY --from=build /src/.build/release/SquareNumber /main
ENTRYPOINT [ "/main" ]
As we can see from the Dockerfile, we need the swift:5.3.2-amazonlinux2 docker image to build the lambda docker image. Because we can have problem with pulling that from the docker public registry from within AWS, I pulled the docker image locally to my Mac, and pushed it to the public ECR repository in AWS:
Login to the public ECR repository:
aws ecr-public get-login-password --region us-east-1 | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin public.ecr.aws
Pull swift.5.3.2-amazonlinux2 (or newer), and push it to the public ECR:
docker pull swift:5.3.2-amazonlinux2
You can create a new public repository with:
aws ecr-public create-repository --repository-name swift --region us-east-1.
The result from the command gives you the url to the public swift repository you created, and you can now push to it. Use your own url in the next command:
docker push public.ecr.aws/o8l5c1i1/swift:5.3.2-amazonlinux2
Push code to GitHub
The pipeline needs to pull the code from a git repository. I chose GitHub, but CodeCommit can also be used. Create the repository in GitHub, I chose the name SquareNumberCICD for my project. Follow the instructions in Github for pushing an existing repository from the command line:
git remote add origin https://github.com/<github-id>/SquareNumberCICD.git
git add .
git commit -m "Initial commit"
git branch -M main
git push -u origin main
You can check the complete code at my repo here: https://github.com/imyrvold/SquareNumberCICD.git.
You also need to make a Personal access token in GitHub. Go to Settings/Developer settings/Personal access tokens and click on the Generate new token button. Click on the first checkbox repo Full control of private repositories, or choose a more restrictive access for your token. Click on Generate token and copy the token to your clipboard.
Setup Secrets manager to retrieve source code from GitHub
Go to AWS Secrets Manager console in AWS, and click on Store a new secret. 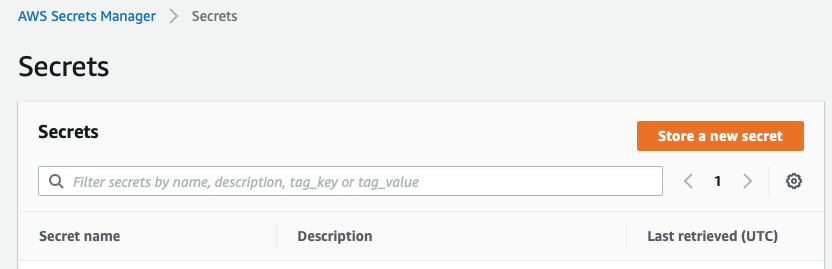 Choose
Choose Other type of secrets and Plaintext, and clear the textfield and paste in the token from clipboard. Click next and choose a secret name. I chose github-token. Now you can just click next till the end, and click store. The secret name and repo is used in square-number-cicd-infra.ts, in sourceAction:
oauthToken: cdk.SecretValue.secretsManager('github-token'),
If you chose another name in Secrets Manager, you have to change it here as well. If you chose another name for the repository itself, you have to change that also:
repo: 'SquareNumberCICD',
Deploy to AWS
Make sure that we don't have any errors in our setup, and that the CDK code can be translated to CloudFormation:
cdk synth
This should print out over 850 lines with CloudFormation to the console.
Before we can deploy, we must bootstrap to add additional functionality for the cdk pipeline to work:
cdk bootstrap \
--cloudformation-execution-policies arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AdministratorAccess \
aws://<AWS account id>/eu-west-1
If you open the CloudFormation AWS Console, you will se after a while that the bootstrap has installed a CDKToolkit. And in the S3 AWS Console, you will see that a new bucket has been added.
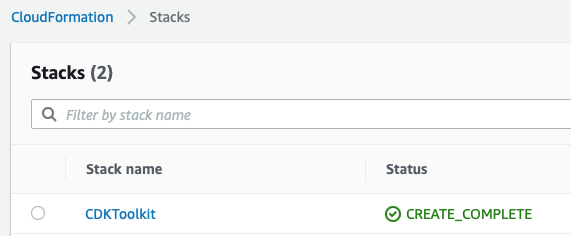
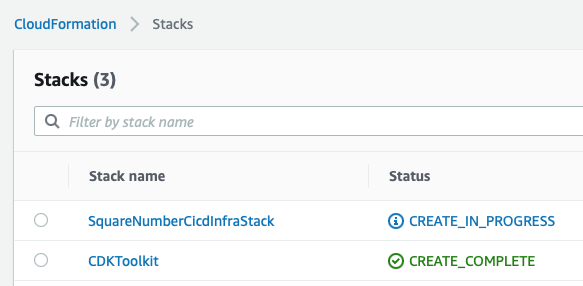
Now we can deploy. Enter y when asked:
cdk deploy
We see that a new stack has been created in CloudFormation:
If we open CodePipeline console, we will see that the pipeline is in progress:
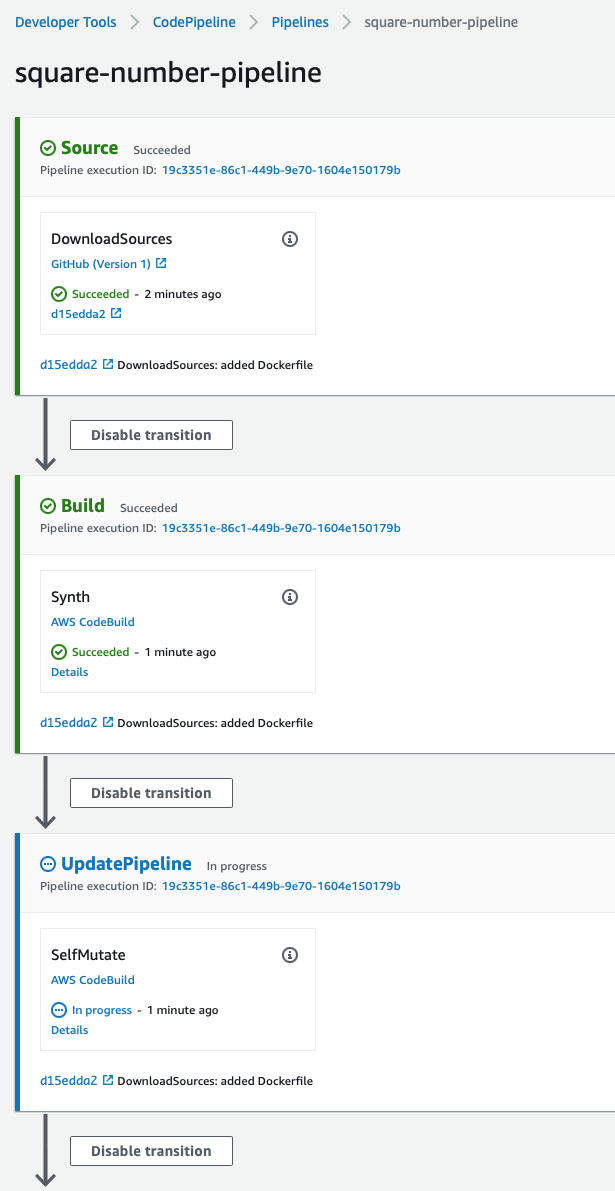
The Source stage pulls the source from GitHub. If anything fails here, it could be that the github token is not correct, or Secrets Manager is not set correctly. The Build stage builds the infrastructure that we defined in square-number-cicd-infra.ts. The 'UpdatePipeline` stage will modify the pipeline if we adds or removes any stage.
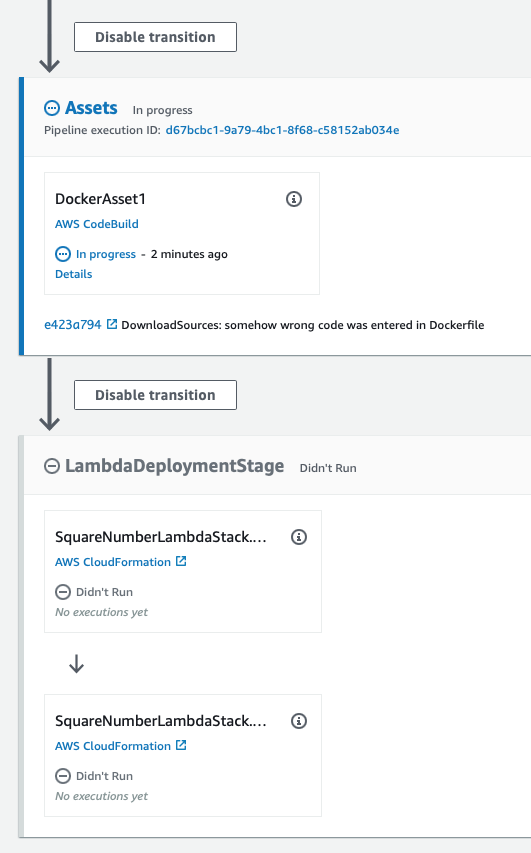
The Assets stage will compile the swift code in Sources/SquareNumber/main.swift, and create the image for deployment of the lambda function. The LambdaDeploymentStage deploys the lambda function to AWS.
Testing the deployed Lambda function
When all the stages of the pipeline have successfully completed, we can test the lambda function SquareNumber. Navigate to the API Gateway: 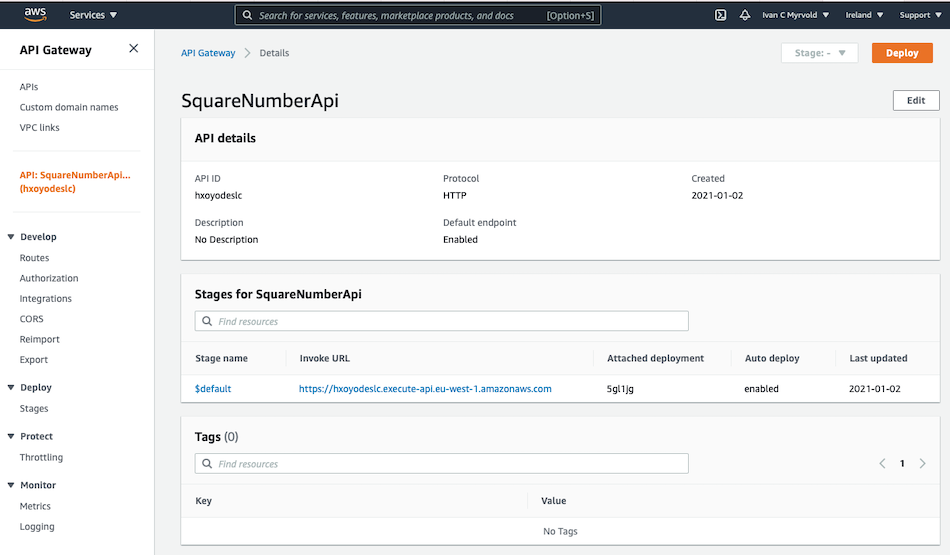
Copy the Invoke URL from the web page, and try the following curl: 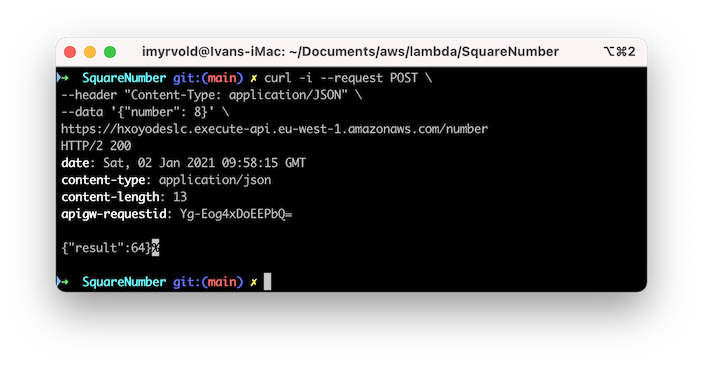
The result of the command is 64, which is the square of the input we sent. The lambda function works.
Conclusion
We now have Lambda function deployed to AWS, and any changes we commit and push to the Swift source code will result in a revised Lambda function to be deployed. We can also test the code locally before we push, so that we can be sure that the lambda function works as planned.
We can also make changes to the CDK infrastructure code, and when we push this to the repository the pipeline will change and self-update. The Cloud Development Kit is an amazing framework to work with. The only thing I wish for is that it in the future it will also support Swift.